Email authentication can make or break your campaign. Email communication is a vital part of any business strategy, but it's not just about writing a compelling message. Your email performance depends on reaching your intended audience in the first place.
With email service providers (ESPs) continually tightening their requirements to filter out spam and phishing attempts, email deliverability becomes increasingly challenging for senders. Email authentication isn't just an optional layer of security anymore — you must verify your emails to reach your subscribers’ inboxes.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through email authentication standards, share up-to-date requirements by ESPs, list the consequences of failing to verify your email domain ownership, and share the best practices for authenticating your emails painlessly.
What is email authentication?
Email authentication is the process of verifying domain ownership by the email sender. It validates you have rightful access to the email address you’re sending from, and you haven’t stolen it from someone else.
There are four email verification methods:
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
- DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail)
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance)
- BIMI (Brand Indicators for Message Identification)
Not familiar with these protocols? Let’s explain each in detail.
Understanding email authentication protocols
Whether you’re setting up email authentication manually or using a dedicated tool, you need to understand the core terminology.
DNS
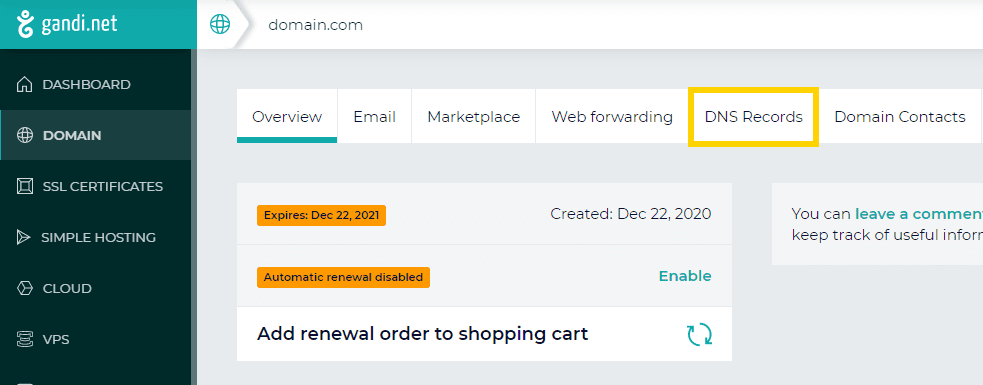
A DNS record, short for Domain Name System record, is a database record used to map domain names to IP addresses and other information associated with a domain. They can be different types, but email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC use TXT (text-based) DNS records. You can access your domain’s DNS records in your domain hosting platform.
Accessing DNS records on the Gandi hosting platform
SPF
SPF is an email authentication method built around a list of IP addresses associated with a given domain. Only they have the right to send emails on behalf of that domain.
Back to SPF, it requires defining a specific DNS record for a domain, listing the authorized email servers that are allowed to send emails on behalf of that domain.
The mail server you’re sending to checks your domain’s SPF record. If the sending server's IP address matches one of the authorized IP addresses listed in the SPF record, the email is considered authentic. If not, the email may be flagged or rejected.
Tip: You can use an SPF validation tool like MX Lookup to verify if you’ve set up your SPF record correctly.
DKIM
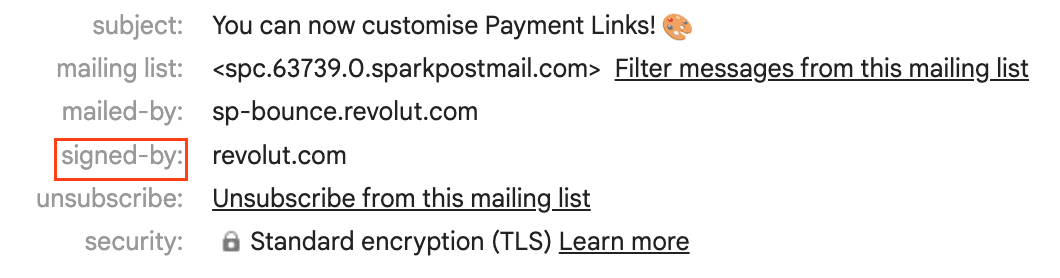
DKIM is another authentication method that adds a digital signature to the email's header using asymmetric encryption.
A DKIM signature example
Here’s how it works:
- The sender generates a pair of private and public keys. The private key is kept secure on the sender's server, while the public key is published in the DNS records.
- When sending an email, the sender’s mail server generates a unique signature based on the email's content and signs it with the private key.
- The receiving server retrieves the public key from the DNS records and validates the signature. If it’s found ok, the email is legit.
DMARC
DMARC is an additional email authentication protocol that goes on top of SPF and DKIM. It lets domain owners provide instructions for email receivers on how to handle emails that fail authentication checks. For instance, you can specify if you want unauthenticated emails to be rejected or quarantined (sent to the spam folder).
DMARC also reports on email authentication so domain owners are aware of issues like spoofing attempts.
Tip: It’s recommended that you set your DMARC policy to ‘p=none’ before you confirm that your legitimate emails don’t fail authentication checks accidentally. When you’re sure the process works properly, you can change it to “quarantine” or “reject”.
In detail: Learn how to configure your SPF, DKIM record, and DMARC in just a few steps.
BIMI
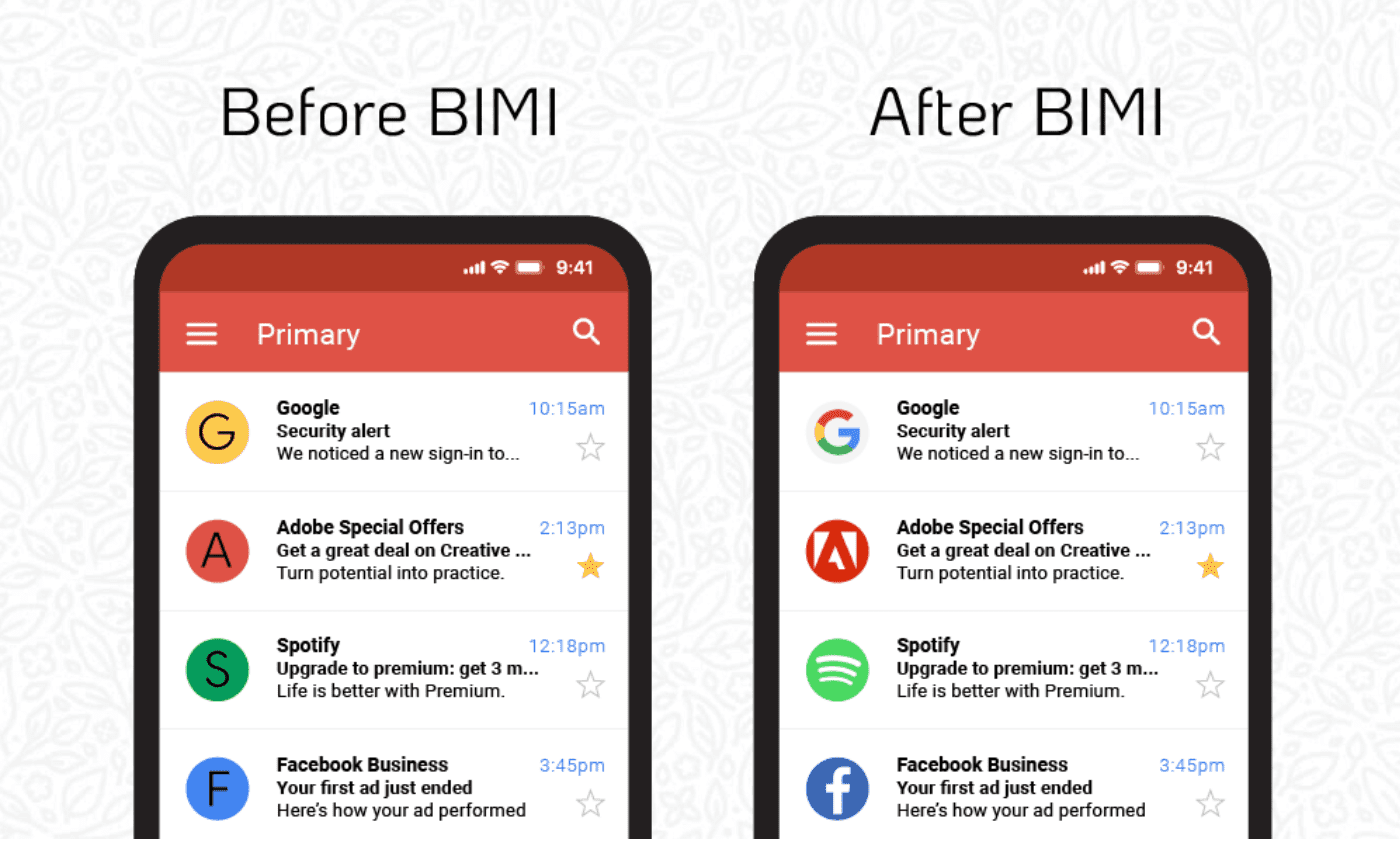
BIMI is an authentication method that enhances your sender trust with a recipient.
It displays your brand’s logo next to the email in the recipient's inbox if the email passes DMARC authentication checks.
Contrary to DKIM or SPF authentication, BIMI isn’t required by any email service provider. However, it boosts your credibility in recipients’ eyes and may improve your email engagement — almost half of worldwide users consider an email safe when it contains familiar branding.
Important: BIMI is currently supported by a few email providers, including Gmail, Yahoo, and Fastmail, but it’s not available in Outlook.
You can implement BIMI authentication only after you’ve set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. Here’s how:
- Upload your logo image (in SVG format) to your public server.
- Check out the requirements of your email service provider. For instance, Gmail requires having a Verified Mark Certificate (VMC). You can only get it if you’ve registered your logo as a trademark.
- Add a BIMI record to your DNS record. You can format a TXT record using this BIMI generator.
- Once you’re all set, you can check your BIMI record using the same tool.
Source: BIMI Group
Which email authentication method is right for you?
You can, and often should, use multiple email authentication methods at the same time. Combining authentication methods strengthens your email security and deliverability.
Different authentication methods serve different purposes. SPF helps prevent email spoofing, DKIM verifies the integrity of the email's content, and DMARC aligns SPF and DKIM results and specifies how failed emails should be handled. Using all of them provides comprehensive protection against various risks.
What if you don’t set up email authentication?
If the process of verifying your domain seems complicated, couldn’t you just skip it?
You could, but it comes with consequences for your business.
If you as a domain owner don’t verify your domain, your emails are more vulnerable to various types of email-based attacks. Here are some potential risks associated with failing to set up email authentication:
- Reduced email deliverability. Email service providers and recipient servers often use authentication methods to filter out spam and ensure the integrity of incoming emails. If a domain is not authenticated, legitimate emails from that domain might be flagged as suspicious or spam, leading to reduced email deliverability.
- Cyber attacks. Statista estimates that three in four organizations worldwide have experienced email-based cyber attacks. For instance, email spoofing is a technique where attackers forge the sender's address to make it look as if the email comes from a trusted source. This is a lot easier when the email hasn’t been authenticated and leads to damaging the trustworthiness of your domain.
- Damage to sender reputation. If a domain is frequently used for phishing scams because of the lack of authentication, the domain's reputation suffers. As a result, email providers blacklist the domain, making it difficult for any emails from that domain to reach recipients' inboxes.
It's crucial to implement email authentication methods not only to protect your organization and subscribers — in fact, recent regulations from the most popular email service providers make authentication of bulk emails obligatory.
Email authentication requirements by service provider
Every email service provider establishes certain standards for email authentication. To ensure the high deliverability of your emails, you need to follow the standards of each provider you’re sending emails to.
Here are the most up-to-date requirements by the three major email service providers: Google, Microsoft, and Yahoo.
Authentication requirements by Google (Gmail)
From February 2024, Google enforces tightened rules for email senders to combat spam and protect recipients from unwanted communications. The new mandates require senders that target Gmail inboxes to:
- Verify their emails using SPF or DKIM authentication if daily sending volume is below 5,000 emails.
- Authenticate their emails using SPF, DKIM, and DMARC if sending 5,000 or more emails per day.
- Keep spam rates below 0.3% (for all senders).
- Provide recipients with a one-click unsubscribe option (only for bulk senders).
If you don’t meet these requirements, your email might be marked as spam or not delivered as expected.
Authentication requirements by Microsoft (Outlook)
Email messages sent to Outlook addresses are subject to the general email authentication best practices that apply to most email providers. Microsoft recommends that senders set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to ensure smooth email delivery.
Read more: How to send bulk emails in Outlook
Authentication requirements by Yahoo (Yahoo Mail)
Yahoo has expressed its solidarity with Google and announced changes for all domains and consumer email brands hosted by Yahoo Mail, too.
Beginning in the first quarter of 2024, Yahoo requires all bulk senders to:
- Authenticate using SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
- Send emails only to users who specifically requested it.
- Support one-click unsubscribe and process user requests within two days.
By doing so, Yahoo strives to create a safer email environment for senders and recipients and declutter user inboxes. If you fail to comply with these regulations, Yahoo can’t guarantee your emails will reach their intended audiences.
Why use an email marketing service to authenticate your emails
You don’t need to be a tech expert to set up email authentication for your domain. A trusted email marketing platform will handle the most difficult parts of the process, verifying your domain in a few steps.
But that’s not the only reason to use an email marketing platform to authenticate and send your emails. There are more:
- Infrastructure. Email marketing services have robust email infrastructure and resources, including dedicated IP addresses and domain reputation management. This infrastructure is often optimized for email deliverability and authentication, increasing the likelihood of your emails reaching recipients' inboxes.
- Compliance. Email marketing services are well-versed in email regulations and compliance standards. They ensure that your email campaigns adhere to these regulations, adding a layer of credibility to you as a sender.
- Email deliverability reports. These services provide detailed reports and analytics about your email campaigns, including delivery rates, open rates, and bounce rates. They can also provide insights into email authentication failures, helping you identify and address any issues promptly.
- Security. Email marketing services invest in security measures to protect their infrastructure and, consequently, your emails. They employ measures like encryption, firewalls, and authentication protocols to safeguard your email communications.
- Enhanced deliverability. Proper authentication improves your email sender reputation. Email marketing services, with their established reputation, can contribute significantly to higher email deliverability rates. ISPs (Internet Service Providers) are more likely to trust emails coming from reputable marketing platforms.
- Easy authentication setup. Most importantly, email marketing platforms like Brevo have established user-friendly processes for implementing email authentication records like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, making it easier for users without much technical expertise.
An email marketing service like Brevo not only makes email authentication easier for non-tech people but also improves your email deliverability and customer trust.
Verify your sender identity with Brevo
Brevo is an ultimate marketing suite that helps you manage your customer communications across email, SMS, WhatsApp, chat, and more. The platform lets you create automatically authenticated email campaigns, ensuring optimal deliverability and increased protection.
Brevo takes you through the whole email authentication process step by step.
- You add your domain name.
- You’ll get the DNS records (Brevo code and DKIM) displayed that need to be added to your domain host.
- The authentication check is carried out for you and after 24-48 hours you get a green check next to the DKIM record.
From then on, your emails will be signed with your domain name, instead of the default Brevo signature.
Can you set up SPF in Brevo?
As a Brevo user, you don’t need to set up an SPF record to enable DMARC.
No need to worry about email authentication
Email marketing is more than choosing a good-looking email template or finding the best time to send your messages. To get your emails delivered and seen, you need to comply with security requirements in the first place.
With Brevo, you have the power to not only craft beautiful emails but also get them in your subscribers' inboxes.
Brevo makes the email authentication process easy. With your sender identity secured, you can confidently build your email strategy.